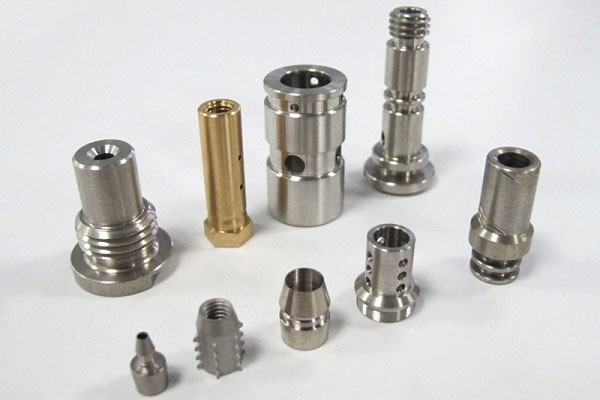
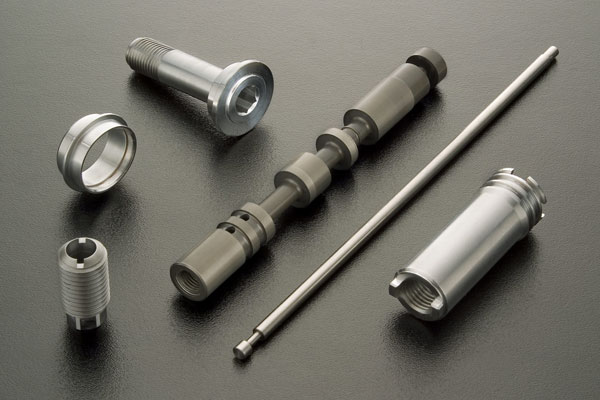
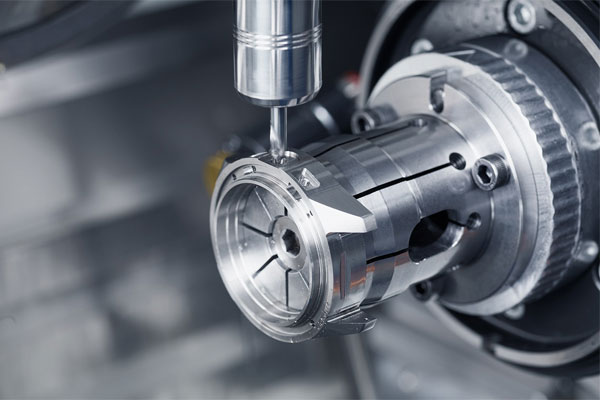
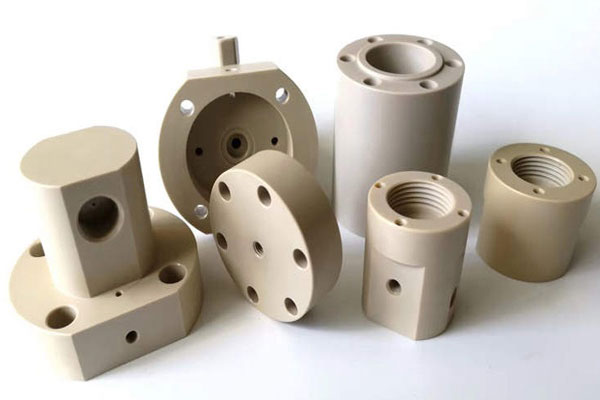
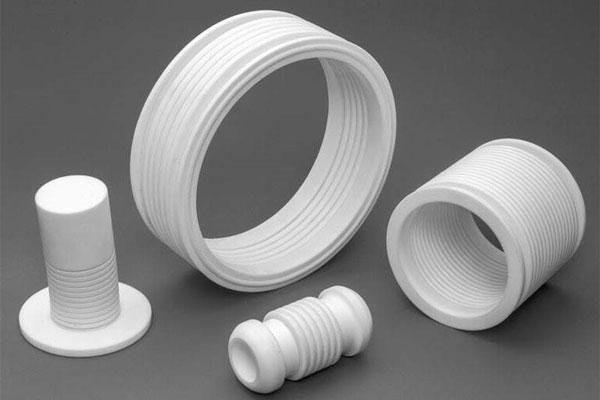
Swiss Machining Services
- Swiss machining (also known as Swiss-type turning) is a highly precise manufacturing process, known for its ability to produce small, complex parts with tight tolerances.
- Contact us to discuss how we can support your manufacturing needs with our advanced Swiss machining capabilities.
- Up to 12 Multi-Axis Controls
- Machining Diameter Up to 40mm, Length Up to 800mm
- ±0.001" (0.025mm) Tight Tolerance
- Various Metal & Plastics Material Compatibility
- Cost-effective for High Volums
- Fine Surface Finish Options
Swiss Machining Axis Configuration
In Swiss machining, the number of axes indicates the complexity and versatility of the machine, as well as the type of movements it can perform.
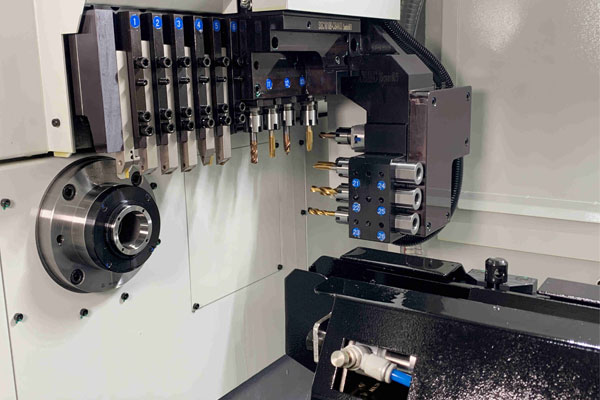

3-Axis Swiss Machining
- Basic Swiss machines with three axes (X, Y, and Z) provide linear motion.
- Suitable for basic cylindrical parts, small holes, and turning operations.
- Cost-effective and faster setup for less complex parts.
5-Axis Swiss Machining
- Adds rotational movements (usually A and B axes) to the basic 3-axis configuration.
- Handle more complex geometries with angled cuts and multi-surface machining.
- Reduces setups and allows for machining multiple surfaces without repositioning.
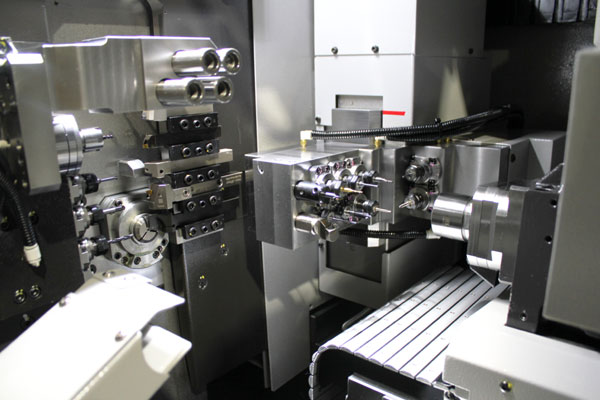

6-Axis Swiss Machining
- Introduces an additional rotational axis or a secondary tool post, improving flexibility.
- Enhanced control over the workpiece and tooling, allowing for more intricate shapes.
- Reduces the need for additional machining steps and fixtures, improving speed.
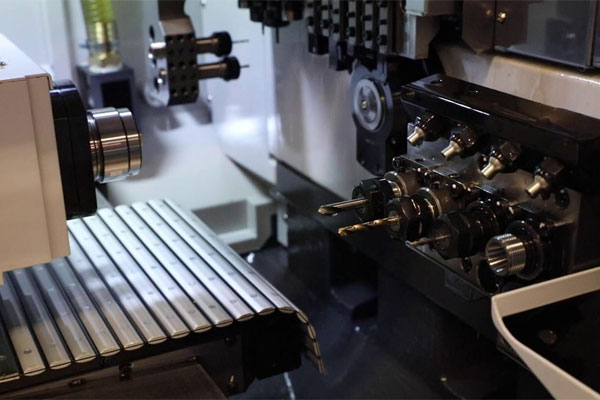

7- Axis Swiss Machining
- Adds yet another rotational or linear axis, involving a second spindle or tool post.
- Offers higher flexibility, handling complicated designs with fewer setups.
- Maximizes productivity, and produces highly complex parts in a single setup.
Swiss-type vs Conventional CNC Turning
This chart highlights the strengths and limitations of each CNC turning approach, helping in selecting the right technology for specific project requirements.
Feature | Swiss-Type CNC Turning | Conventional CNC Turning |
Primary Use | Small, complex, high-precision parts (e.g., medical devices, electronics) | Larger, less complex parts in general industrial applications |
Workpiece Support | Workpiece is supported by a guide bushing, allowing for long, thin part machining with minimal deflection | Workpiece is held at one or both ends, limiting length-to-diameter ratio |
Precision | Extremely high precision (often within microns), ideal for intricate details | High precision but generally not as fine as Swiss-type machines |
Material Handling | Better suited for continuous bar stock; works well with smaller diameters | Handles larger diameter materials and a wide range of part sizes |
Tooling Configuration | Multi-axis (up to 12) allows for simultaneous operations | Fewer axes, often restricted to 2-5 axes |
Cycle Time | Faster for complex and intricate parts | Slower when dealing with parts that require many different operations |
Setup Complexity | More complex setup and requires skilled operators | Easier setup, generally more operator-friendly for simpler parts |
Applications | Medical, aerospace, electronics, watchmaking, and automotive industries | General industrial parts, automotive, oil & gas, heavy machinery |
Cost | Higher machine cost and operational costs, but efficient for high-volume production of small parts | Lower machine cost but may require more time for complex parts |
Materials for Swiss Machining
Aluminum | 6061 | 5052 | 2024 | 7075 | 5086 |
Stainless Steel | 303 | 304 | 316 | 17-4PH | |
Brass | C36000 | C38000 | C38500 | C27000 | C27200 |
Copper | C10100 | C11000 | C14500 | C36000 | |
Titanium | Grade 2 | Grade 5 | Grade 6Al-4V ELI | Grade 9 | |
Tool Steel | D2 | O1 | A2 | M2 | S7 |
Carbon Steel | 1018 | 1045 | 1060 | 1095 | 12L14 |
Inconel | 600 | 625 | 718 | ||
Plastics | PEEK | PTFE | Delrin® | Nylon | Polycarbonates (PC) |
Our Swiss Machining Projects